Yes, modern energy storage batteries can charge from the grid when properly configured. Grid charging allows batteries to store electricity during off-peak periods and discharge it when needed, improving energy reliability, cost control, and backup capability for residential and commercial users.
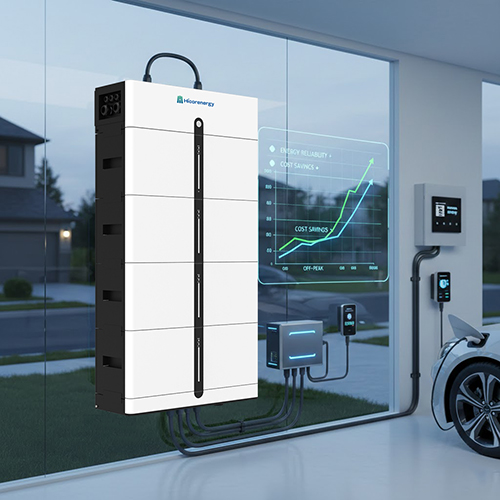

Understanding Battery Charging Basics
Battery charging is the process of converting electrical energy into chemical energy stored within battery cells. When a system is designed to support Battery Charge from the Grid, electricity from the utility network flows through an inverter and battery management system to ensure safe voltage, current, and temperature levels. Proper charging control protects battery health, maximizes cycle life, and ensures stable performance, regardless of whether energy originates from solar, the grid, or hybrid sources.
Types of Batteries Capable of Charging from the Grid
Not all batteries are equally suitable for grid charging. According to industry practices reflected by solutions available at hicorpower.com, lithium-ion batteries—especially LiFePO4 chemistry—are the most widely used for Battery Charge from the Grid. These batteries offer high efficiency, long cycle life, fast charging capability, and strong thermal stability. Compared with traditional lead-acid batteries, lithium-based systems support deeper discharge and more frequent grid charging without significant degradation. As a result, they are commonly used in residential energy storage, commercial and industrial systems, and grid-support applications where flexibility and reliability are critical.
Grid-Tied vs. Off-Grid Battery Systems
Grid-tied and off-grid battery systems differ significantly in how they interact with the utility network. Grid-tied systems are directly connected to the grid, enabling seamless Battery Charge from the Grid during low-tariff periods or when renewable generation is insufficient. Off-grid systems, by contrast, operate independently and typically rely on solar or generators, though some hybrid designs still allow controlled grid charging. Understanding these distinctions helps users select a system that balances energy independence, cost efficiency, and operational stability, making this comparison a key transition point for deeper evaluation.
Benefits of Charging Batteries from the Grid
Charging batteries from the grid offers multiple advantages across residential and commercial scenarios. One major benefit is cost optimization. By enabling Battery Charge from the Grid during off-peak or low-tariff periods, users can reduce electricity expenses and discharge stored energy during peak pricing hours. Grid charging also enhances energy security by ensuring batteries remain charged even when renewable generation is unavailable. For regions with unstable power supply, this approach provides reliable backup during outages. Additionally, grid charging supports peak shaving and load balancing for factories and commercial buildings, helping to reduce demand charges and improve overall energy management efficiency without compromising system performance.
Challenges and Considerations for Grid Charging
Despite its advantages, Battery Charge from the Grid requires careful system design and management. Key considerations include grid compatibility, inverter quality, charging control accuracy, and battery safety. Poorly managed charging can lead to inefficiencies or accelerated battery aging. Hicorenergy addresses these challenges through advanced lithium battery solutions equipped with self-developed battery management systems and intelligent monitoring platforms. Products such as residential and commercial energy storage systems are designed to support controlled grid charging, real-time monitoring, and remote upgrades. These features help users manage charging schedules, maintain optimal operating conditions, and ensure long-term reliability while complying with local grid regulations and safety standards.
Future Trends in Grid Charging Technology
The future of Battery Charge from the Grid is closely linked to digitalization and smarter energy networks. Intelligent algorithms will increasingly automate charging decisions based on electricity pricing, grid demand, and user consumption patterns. Integration with energy management systems and smart meters will allow batteries to respond dynamically to grid signals. Advances in battery chemistry and thermal management will further improve fast-charging capability and lifespan. As virtual power plants and demand response programs expand, grid-charged batteries will play a more active role in supporting grid stability and accelerating the transition to low-carbon energy systems.
Conclusion
Battery Charge from the Grid is a practical and efficient solution for enhancing energy flexibility and reliability. With advanced lithium battery technology and intelligent management features, Hicorenergy products support safe, efficient grid charging for residential and commercial energy storage applications.
Contact Information:
Email: info@hicorpower.com
WhatsApp: +86 181-0666-3226